The article “Gated Recurrent Unit Neural Networks for Automatic Modulation Classification With Resource-Constrained End-Devices” by our lab member Ramiro Utrilla has just been published in the IEEE Access, a high-impact open-access journal.
This work has been carried out in collaboration with researchers from the CONNECT – Centre for Future Networks and Communications in Dublin (Ireland), where Ramiro carried out a research stay of 3 months.
In this article, they focus on the Automatic Modulation Classification (AMC). AMC is essential to carry out multiple CR techniques, such as dynamic spectrum access, link adaptation and interference detection, aimed at improving communications throughput and reliability and, in turn, spectral efficiency. In recent years, multiple Deep Learning (DL) techniques have been proposed to address the AMC problem. These DL techniques have demonstrated better generalization, scalability and robustness capabilities compared to previous solutions. However, most of these techniques require high processing and storage capabilities that limit their applicability to energy- and computation-constrained end-devices.
In this work, they propose a new gated recurrent unit neural network solution for AMC that has been specifically designed for resource-constrained IoT devices.
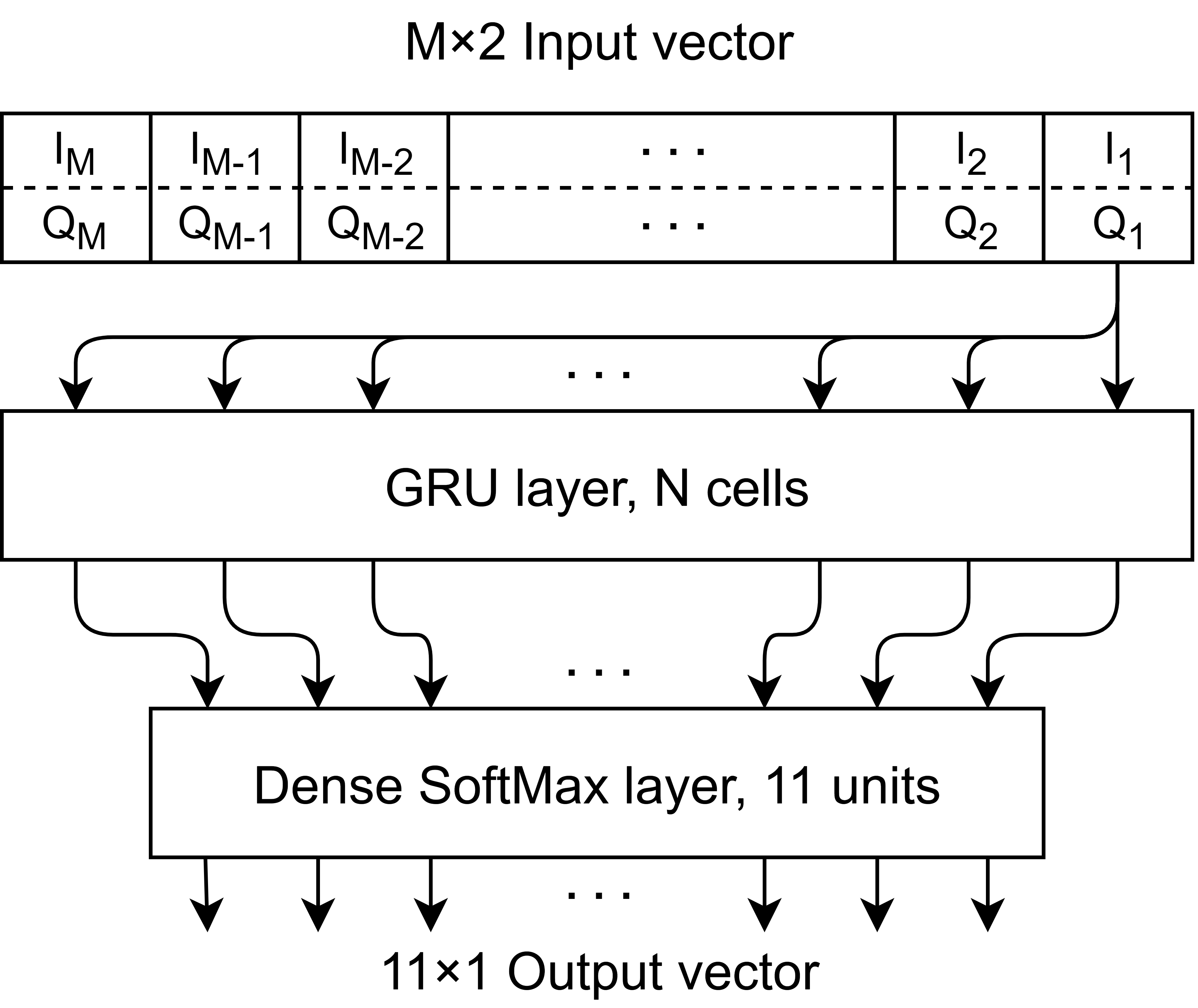
The proposed GRU network model for AMC.
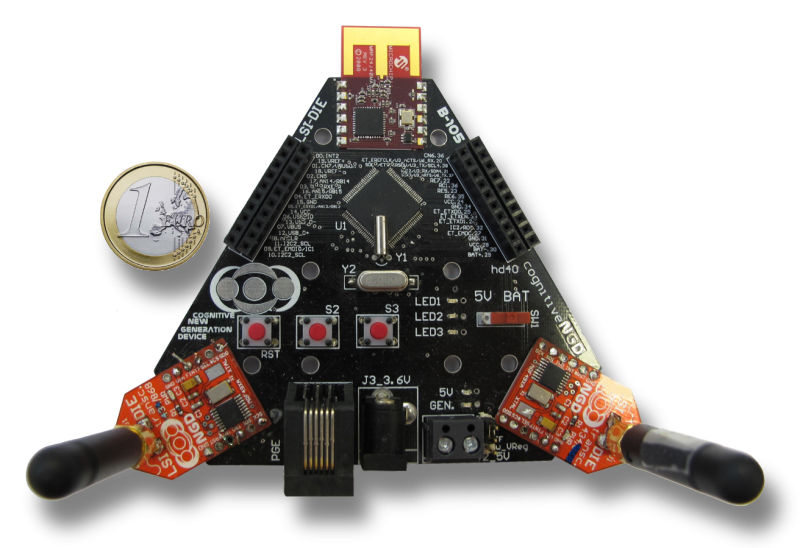
They trained and tested their solution with over-the-air measurements of real radio signals, which were acquired with the MIGOU platform.
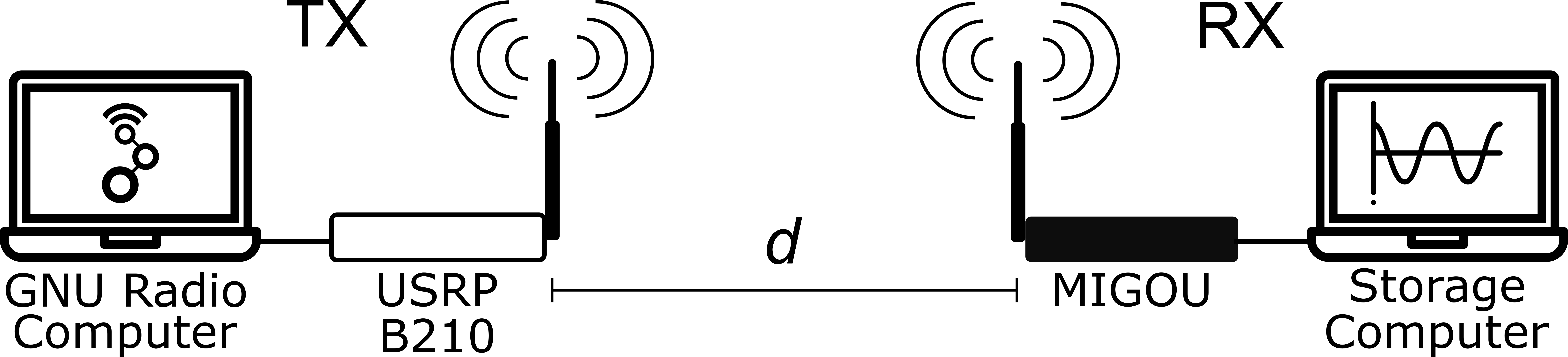
Dataset generation scenario set up.
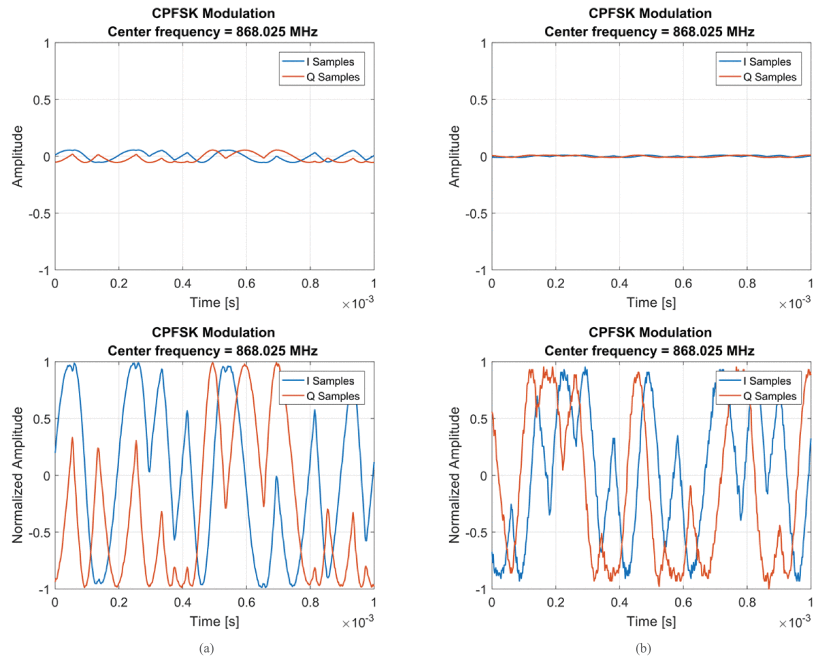
Comparison of signals recorded at (a) 1 and (b) 6 meters. The signals in the bottom row are the normalized version of those in the top row.
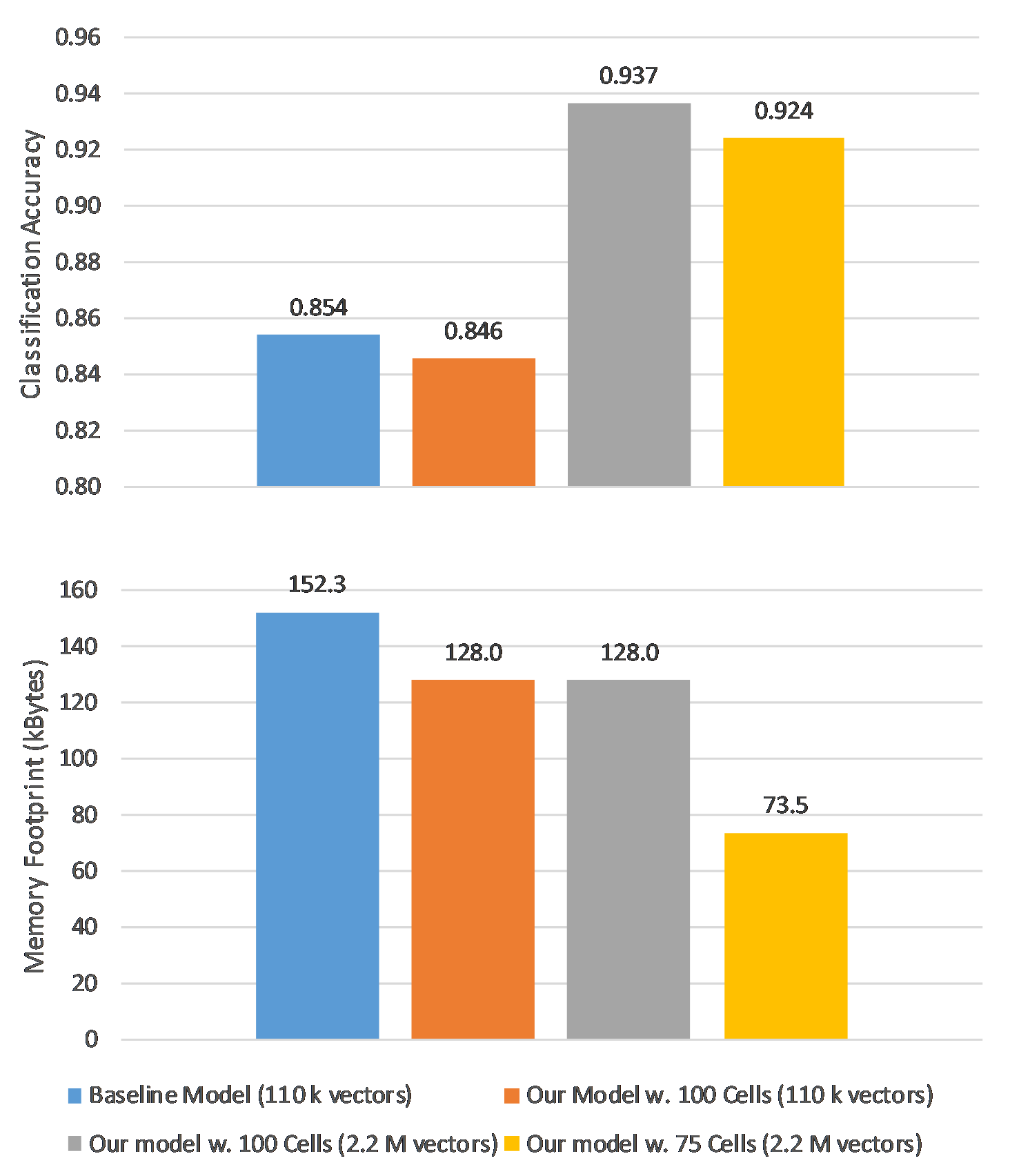
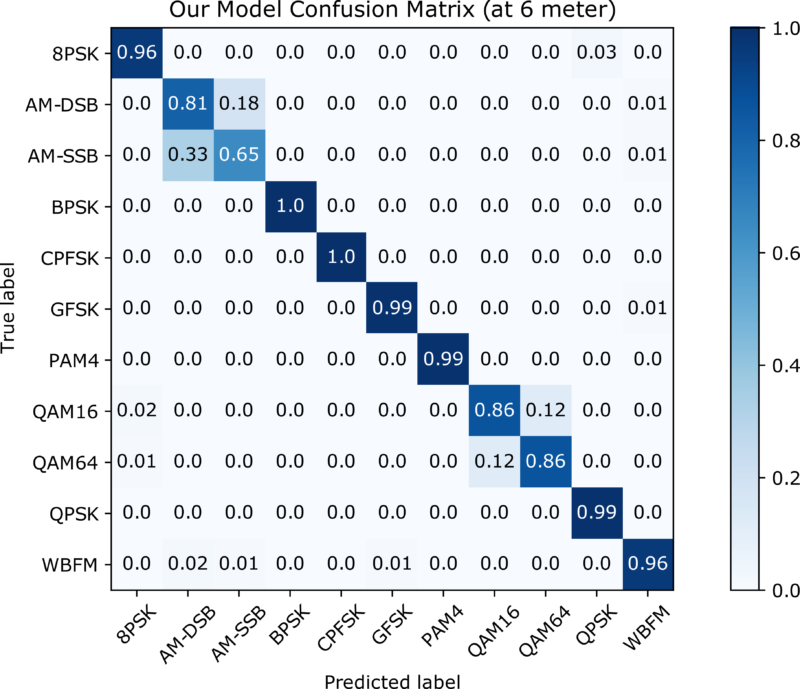
Their results show that the proposed solution has a memory footprint of 73.5 kBytes, 51.74% less than the reference model, and achieves a classification accuracy of 92.4%.