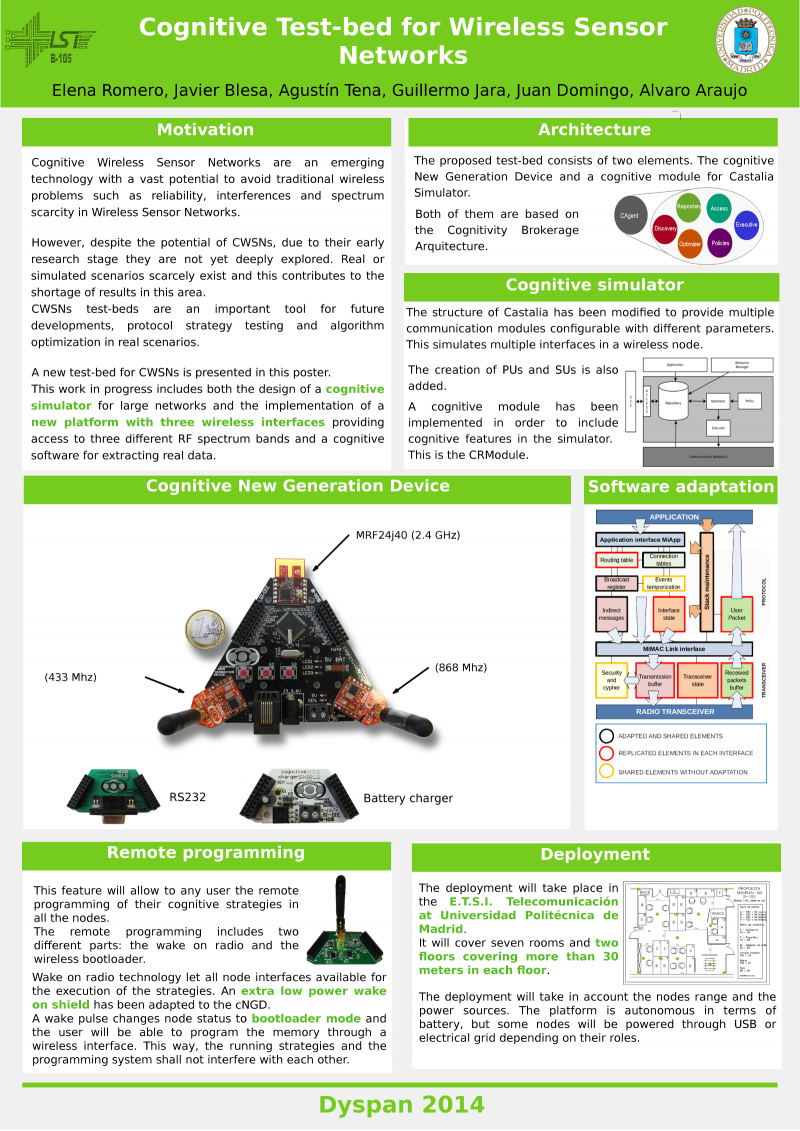
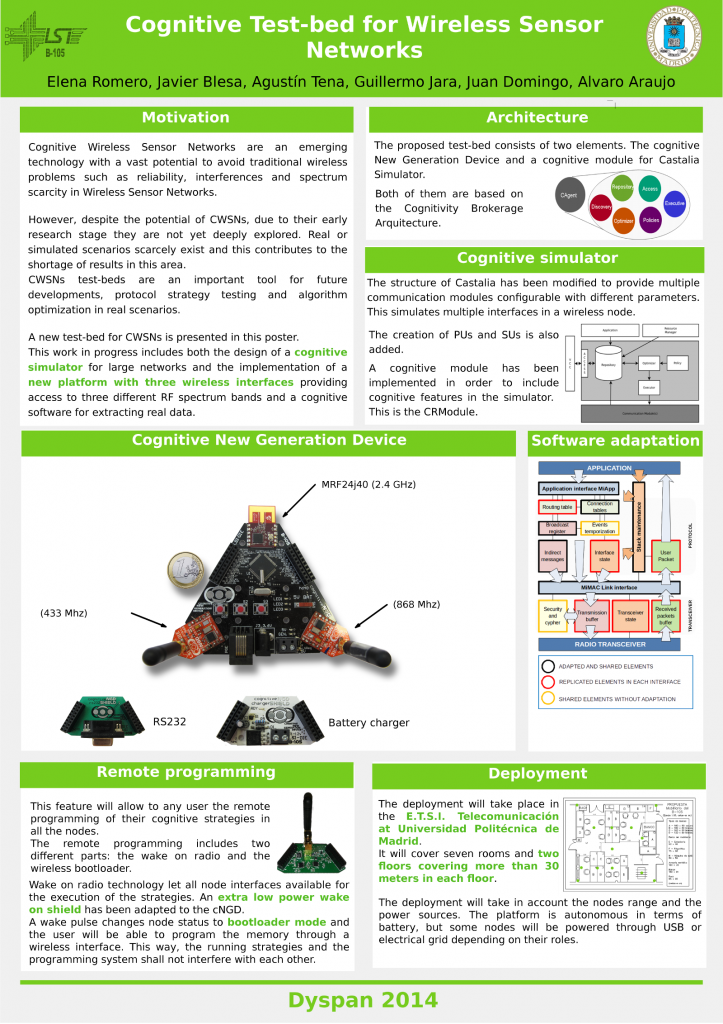
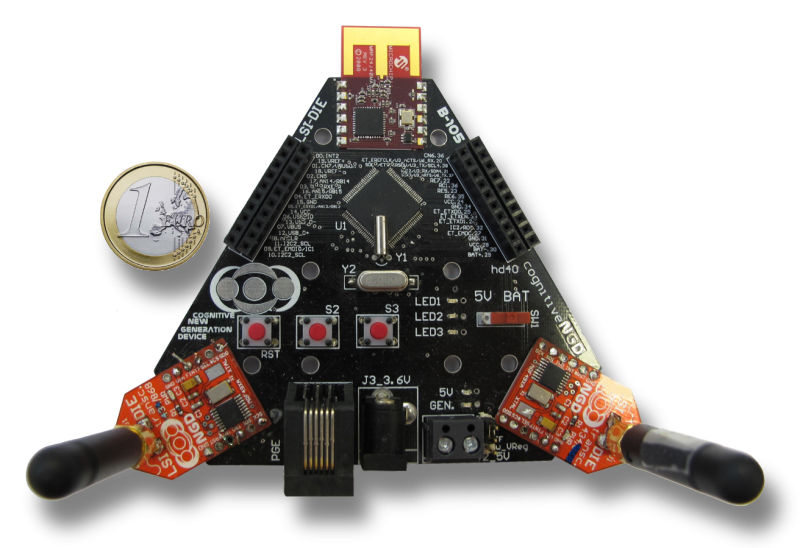
Los miembros del B105 Alvaro Araujo y Alba Rozas han asistido a la International Wireless Comunications and Mobile Computing Conference 2015 que ha tenido lugar del 24 al 28 de agosto en Dubrovnik, Croacia. El lema de la edición de este año ha sido Communications for the 21st Century, y las charlas se han centrado en las redes inalámbricas, comunicaciones wireless y computación móvil.
Alvaro ha desempeñado el papel de chair en varias sesiones, mientras que Alba ha presentado su artículo titulado Controlling the Degradation of Wireless Sensor Networks que había sido aceptado previamente. El congreso ha servido para conocer trabajos interesantes de muchas universidades del mundo así como para recibir realimentación sobre la investigación que realizamos en el grupo.
Además, hemos podido establecer contacto con varios investigadores extranjeros de nuestro campo. De hecho, los profesores Hacène Fouchal y Milena Radenkovic, de las universidades de Reims en Francia y de Nottingham en Reino Unido respectivamente, han sido invitados como informantes y miembros del tribunal en las tesis de Elena Romero y Javier Blesa, cuya lectura está prevista para el próximo mes de octubre.