TFM: Development of an electronic system on smart garments to aid in the diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases
Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects the nervous system, which mainly causes motor disorders. It affects more than 160,000 people in Spain. In addition, it is expected that due to the growing aging of the population it will become the most common serious disease by the year 2040.
One of the main problems faced in this disease is the delay in its diagnosis. In addition, it is important to ensure that patients’ symptoms are properly monitored in order to correctly adjust their medication.
Over the past few years, the use of wearable devices to monitor patients outside of the hospital environment has increased. Among these devices, those that use sensorized clothing, so that the sensors are integrated into the tissues, are gaining popularity and have great potential. Although these are still at an early stage of development.
In this context begins this Master’s Thesis, which is part of the research line of the B105 Electronic Systems Lab for the development of wearable devices. The main objective of the project is to design and implement an electronic system to control a set of intelligent clothes for the monitoring of different parameters, which can be connected to other wearable devices in the future.
For this purpose, a study of the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease and how it is possible to monitor them have been carried out. We have also analysed which studies have been conducted in recent years using textile sensor to diagnose or monitor this pathology. Subsequently, it has been searched which intelligent garments are being commercialized in the market. And finally, it has been established which requirements are intended to be fulfilled by the design that is going to be carried out.
Due to the initial work done, the design of the system to be implemented has been carried out.
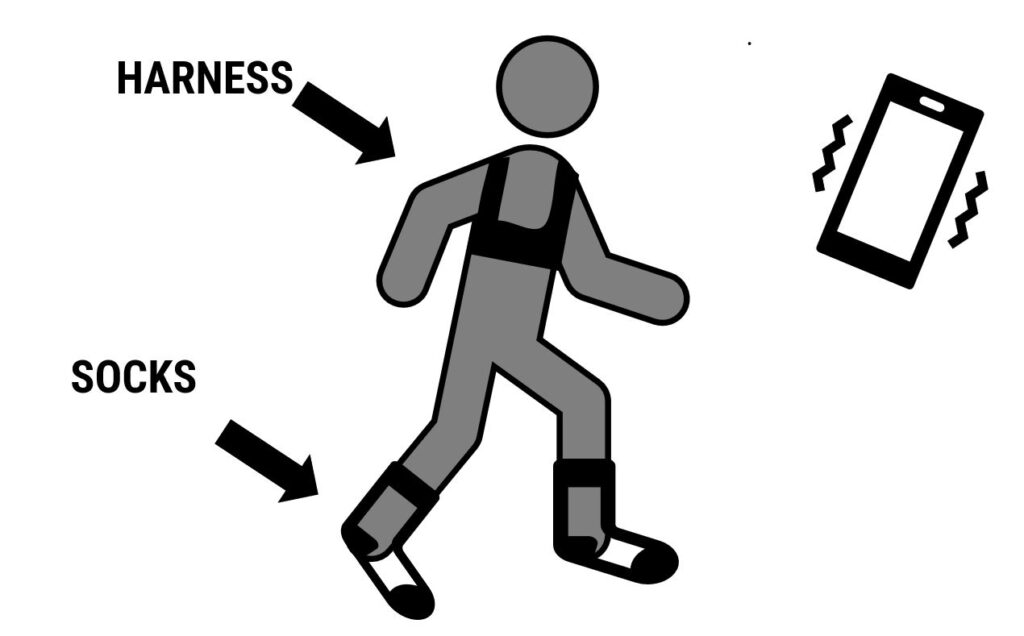
It consists of a pair of socks and a harness, which communicate through Bluetooth with a mobile phone application.

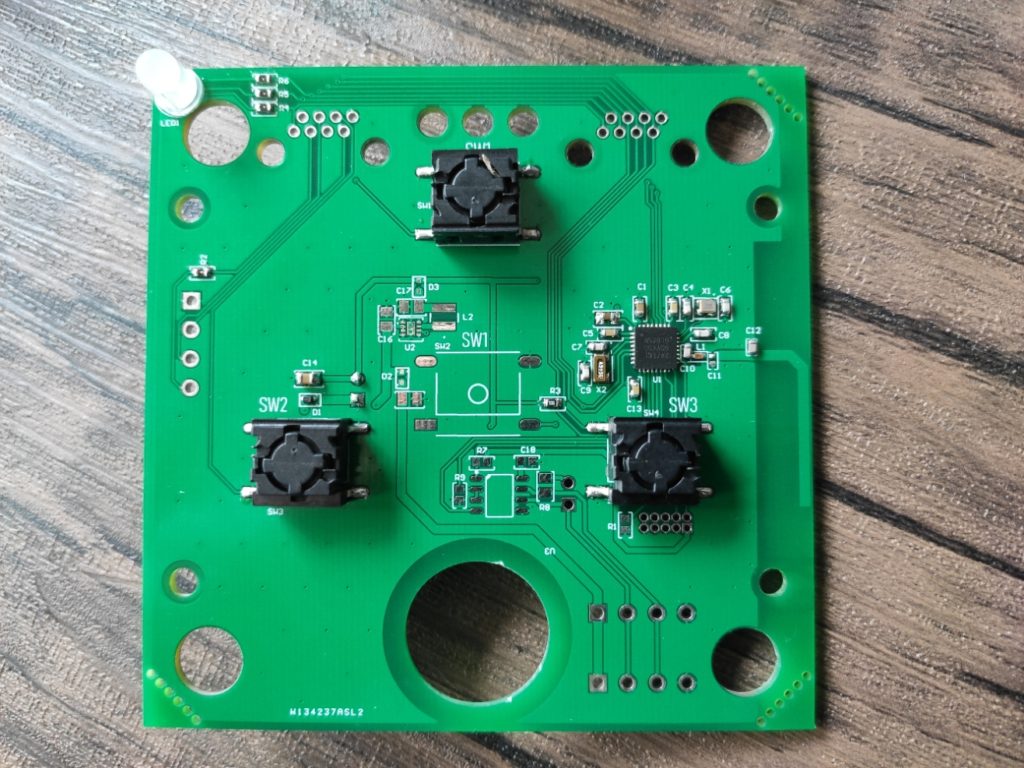
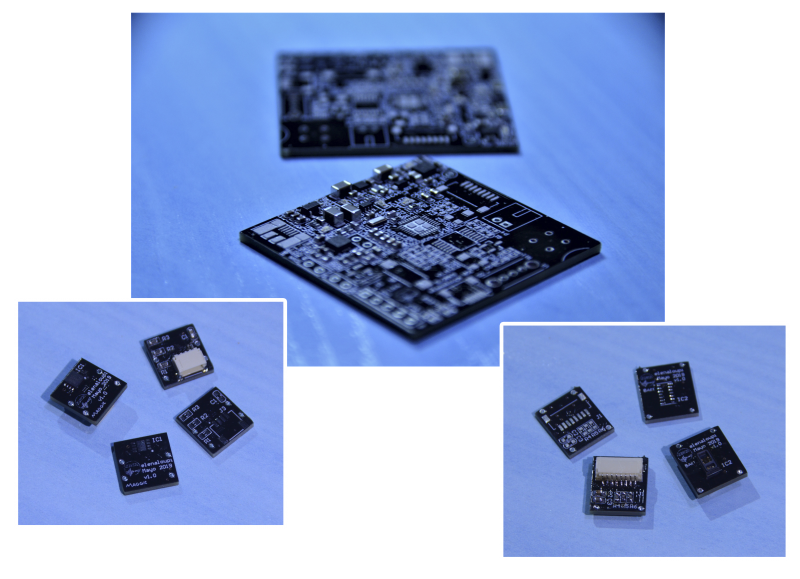
The socks incorporate 3 textile resistors in the sole of the foot, and an IMU in the ankle to monitor the patient’s gait. While the harness makes use of 3 textile electrodes, whose outputs are filtered by a circuit to obtain the ECG. It also incorporates an IMU in the central part of the chest, to monitor the user’s posture. In addition, both garments make use of a PCB in which they operate the control part and the power supply.
In the software development of the project, FreeRTOS has been used together with a state machine to control the measurements of the sensors of the garments and send the measured values via bluetooth to a mobile application.
Finally, we have started to perform unit tests on the development carried out, for the hardware as well as for the software, which should be finalized to verify the complete performance of the developed system.