Title: Cognitive Test-bed for Wireless Sensor Networks
Authors: Elena Romero, Javier Blesa, Agustín Tena, Guillermo Jara, Juan Domingo and Alvaro Araujo
Published in: IEEE DySPAN 2014
Date of Publication: March 2014
Web: http://dyspan2014.ieee-dyspan.org/
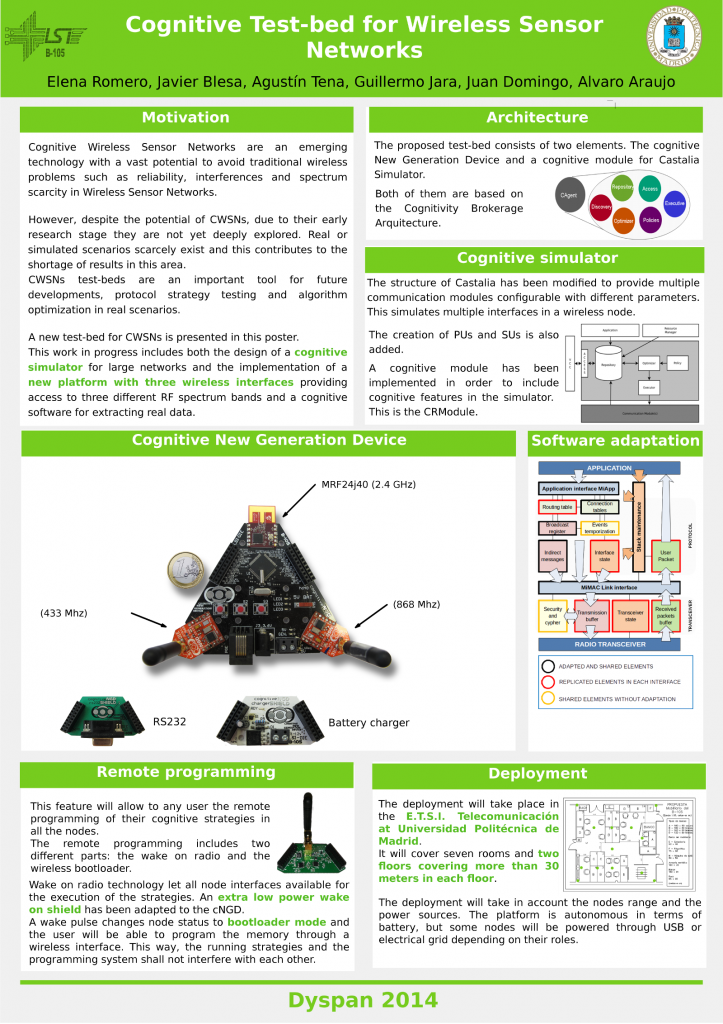 Cognitive Wireless Sensor Networks are an emerging technology with a vast potential to avoid traditional wireless problems such as reliability, interferences and spectrum scarcity in Wireless Sensor Networks.
Cognitive Wireless Sensor Networks are an emerging technology with a vast potential to avoid traditional wireless problems such as reliability, interferences and spectrum scarcity in Wireless Sensor Networks.
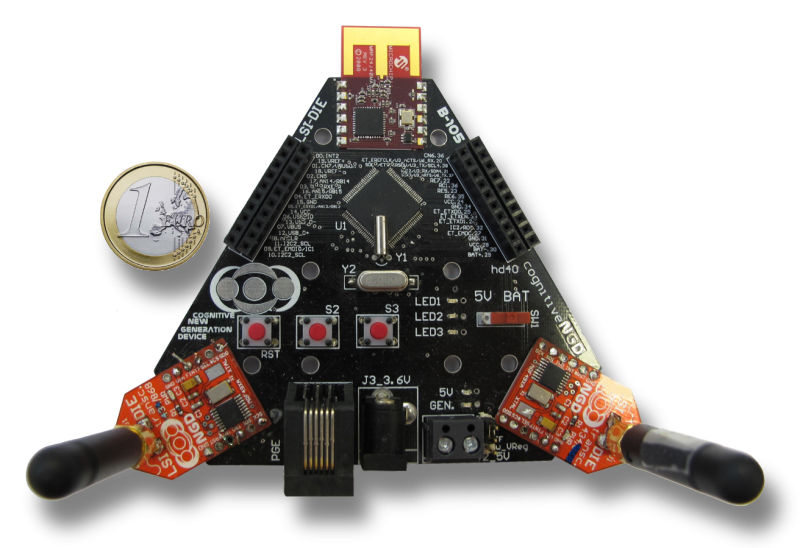
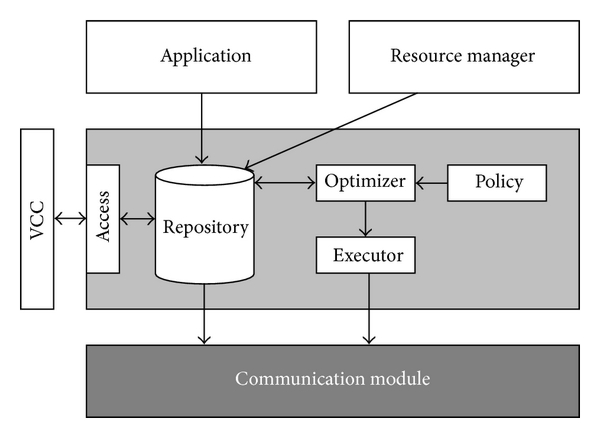
Cognitive Wireless Sensor Networks test-beds are an important tool for future developments,protocol strategy testing and algorithm optimization in real scenarios. A new cognitive test-bed for Cognitive Wireless Sensor Networks is presented in this paper. This work in progress includes the design of both a cognitive simulator for networks with high number of nodes and the implementation of a new platform with three wireless interfaces and a cognitive software for extracting real data.
Finally, as a future work, a remote programmable system and the planning for the physical deployment of the nodes at the university building is presented.