Title: Detecting and confining Sybil attack in wireless sensor networks based on reputation systems coupled with clustering algorithms
Authors: Zorana Bankovic, David Fraga, José Manuel Moya, Juan Carlos Vallejo, Alvaro Araujo, Pedro Malagón, Juan Mariano de Goyeneche, Daniel Villanueva, Elena Romero and Javier Blesa
Published in: Journal Engineering Intelligent Systems, Vol 20, 3
ISSN : 1472-8915
Date of Publication: September 2010
Digital Object Identifier :
Web: http://www.crlpublishing.co.uk/journal.asp?j=eis&s=Recent%20Special%20Issues
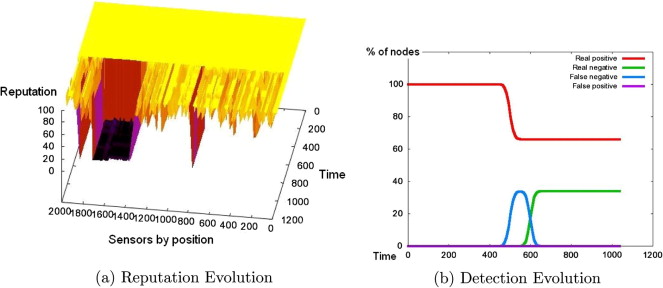
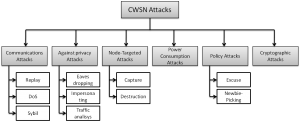
The Sybil attack is one of the most aggressive and elusive attacks in sensor networks that can affect on many aspects of its operation. Thus, its efficient detection is of highest importance. In order to resolve this issue, in this work we propose to couple reputation systems with agents based on clustering algorithms trained for detecting outliers in data. The response of the system consists in assigning low reputation values to the compromised nodes rendering them isolated from the rest of the network. The main improvement of this work consists in the inclusion of distributed detector with redundancy, which provides optimal detector configuration in an autonomous way. Clustering algorithms deploy feature space based on sequences of sensor outputs. Our solution offers many benefits: scalable solution, fast response to adversarial activities, ability to detect unknown attacks, high adaptability and low consumption. The testing results demonstrate its high ability in detecting and confining Sybil attack.