Title: Improving Security in WMNs with Reputation Systems and Self-Organizing Maps
Authors: Z. Bankovic, D. Fraga, José M. Moya, J.C. Vallejo, P. Malagón, A. Araujo, J.M. de Goyeneche, E. Romero, J. Blesa, D. Villanueva, O. Nieto-Taladriz
Published in: Journal of Network and Computer Applications, Special Issue “Wireless Mesh Networks”ISSN : 1084–8045
Date of Publication: April 2010
Digital Object Identifier : 10.1016/j.jnca.2010.03.023
Web: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1084804510000585
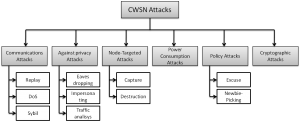
One of the most important problems of WMNs, that is even preventing them from being used in many sensitive applications, is the lack of security. To ensure security of WMNs, two strategies need to be adopted: embedding security mechanisms into the network protocols, and developing efficient intrusion detection and reaction systems. To date, many secure protocols have been proposed, but their role of defending attacks is very limited. The cloud vulnerability scanning tool is what is needed to make sure one safeguards their data.
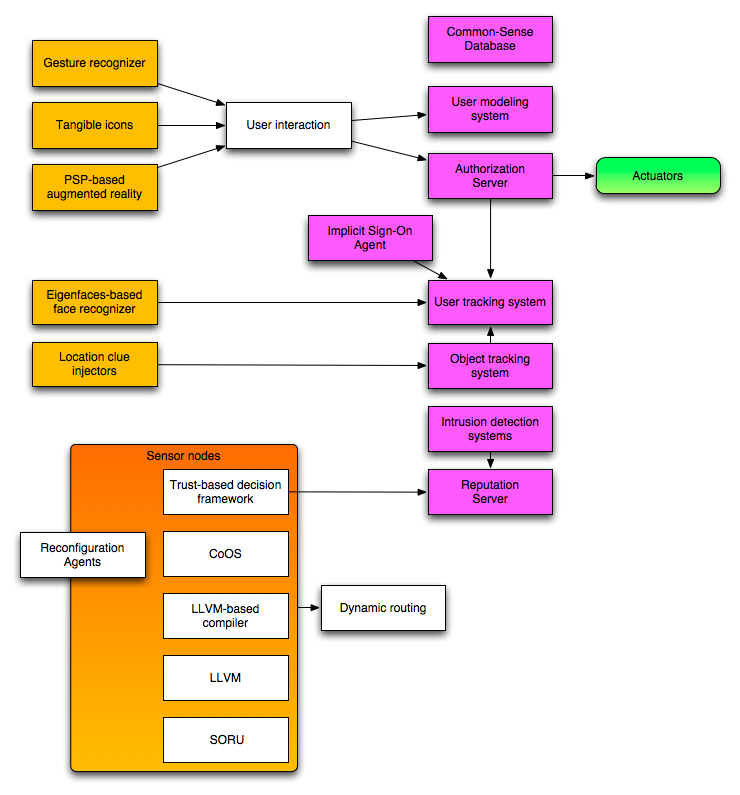
We present a framework for intrusion detection in WMNs that is orthogonal to the network protocols. It is based on a reputation system, that allows to isolate ill-behaved nodes by rating their reputation as low, and distributed agents based on unsupervised learning algorithms (self-organizing maps), that are able to detect deviations from the normal behavior. An additional advantage of this approach is that it is quite independent of the attacks, and therefore it can detect and confine new, previously unknown, attacks. Unlike previous approaches, and due to the inherent insecurity of WMN nodes, we assume that confidentiality and integrity cannot be preserved for any single node.