Title: Distributed Intrusion Detection System for Wireless Sensor Networks based on a Reputation System coupled with Kernel Self-Organizing Maps
Authors: Z. Bankovic´, J.M. Moya, A. Araujo, D. Fraga, J.C. Vallejo, J.M. de Goyeneche
Published in: Integrated Computer-Aided Engineering, Vol 17
ISSN : 1069–2509
Date of Publication: April 2010
Digital Object Identifier : 10.3233/ICA-2010-0334
Web: http://iospress.metapress.com/content/67t2t65423226255/
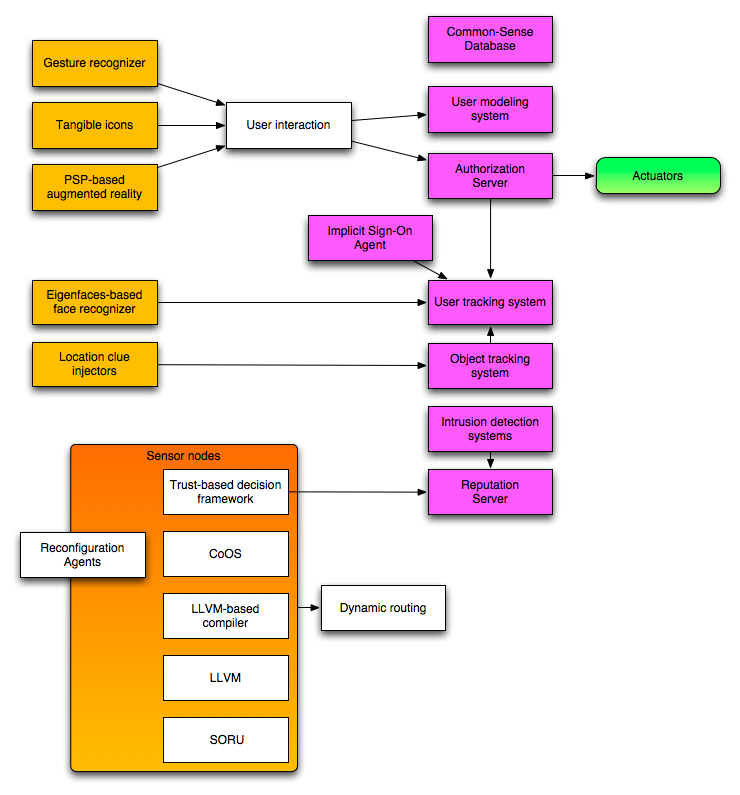
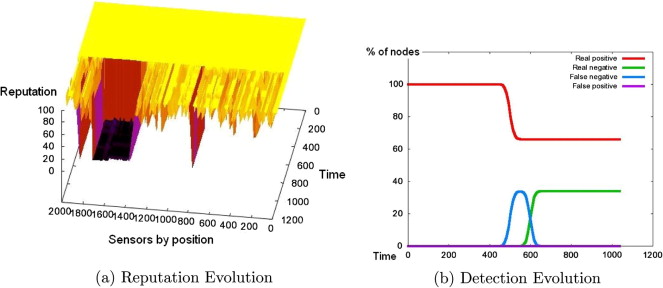
Security of sensor networks is a complicated task, mostly due to the limited resources of sensor units. The first line of defense, i.e. encryption and authentication, is useless if an attacker has entered the system, and it is also vulnerable to side-channel attacks. Thus, a second line of defense, known as Intrusion Detection, must be added in order to detect and eliminate attacks. In the recent past, various solutions for detecting intrusions have been proposed. Most of them are able to detect only a limited number of attacks. Further, the solutions that deploy machine learning techniques exhibit higher level of flexibility and adaptability. Yet, these techniques consume significant power and computational resources. In this work we propose a distributed intrusion detection system organized as a reputation system where the reputation of each node is assigned by self-organizing maps (SOM) trained for detecting intrusions. The response of the system consists in assigning low reputation values to the compromised nodes rendering them isolated from the rest of the network. Further, we propose the implementation of SOM algorithm using the energy-efficient SORU (Stream Oriented Reconfigurable Unit) co-processor developed by our research group. Our solution offers many benefits: scalable solution, fast response to adversarial activities, ability to detect unknown attacks, high adaptability and energy efficiency. The testing results demonstrate its high potential.