El pasado Octubre el B105 realizó una visita a la Mina de San Finx (Galicia). Esta visita se encuadra dentro del proyecto financiado por el CDTI y desarrollado con la empresa Valoriza Minería: Desarrollo de un sistema prototipo automatizado de perforación vertical de barrenos para su aplicación en la industria minera, al que internamente denominamos Robot Minero.
Este tiene como objetivo el desarrollo de un robot capaz de mecanizar el proceso de explotación en minería, aumentando el rendimiento y mejorando las condiciones de seguridad de los operarios. Se realiza, además de con Valoriza Minería, en colaboración con Segeda y ASEMAQ.
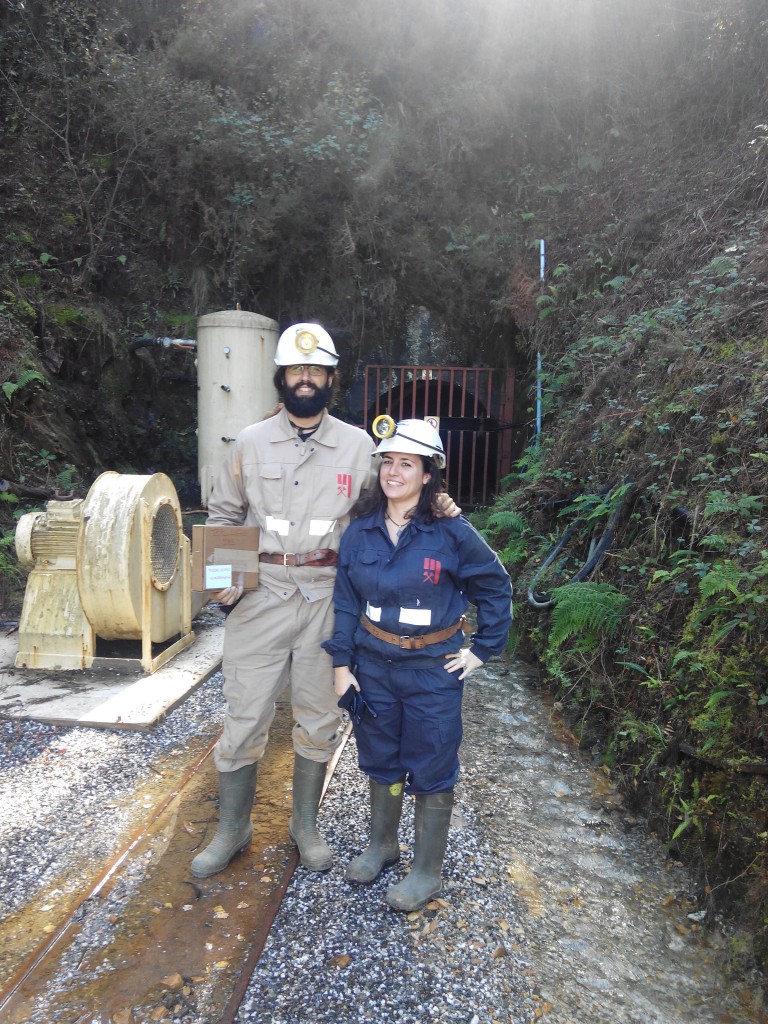
Durante esta visita pudimos comprobar de primera mano las instalaciones de la mina:
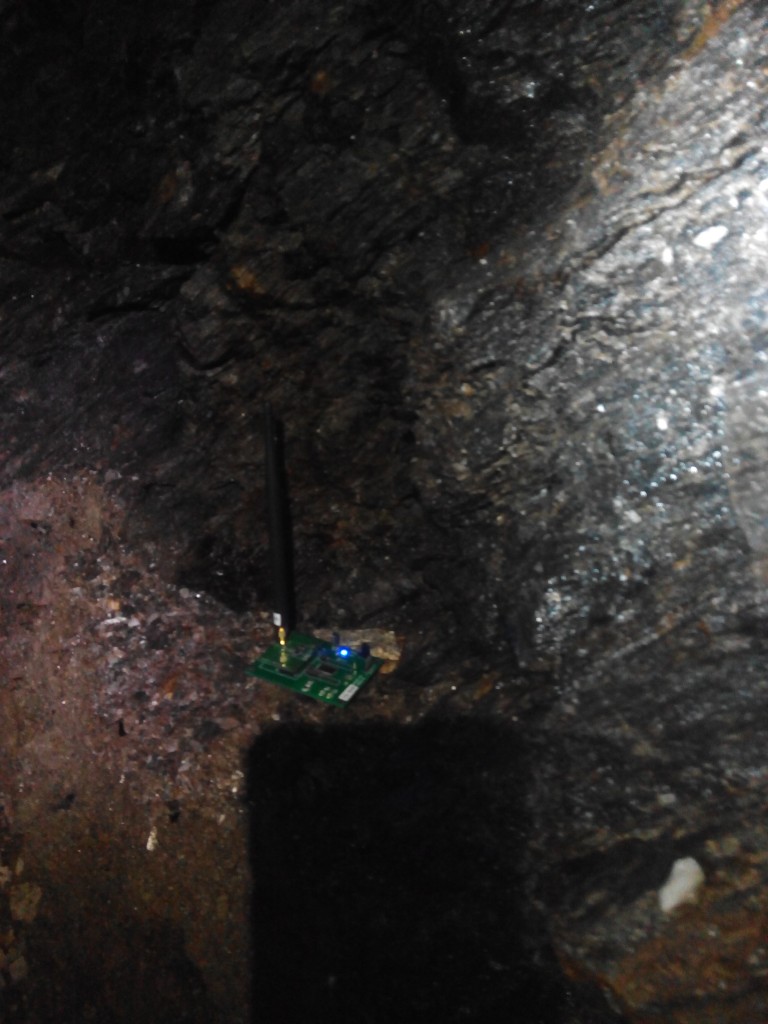
Así como realizar diferentes pruebas de comunicaciones inalámbricas en el interior de la mina:
Por último, pudimos hablar con los trabajadores para obtener sus necesidades de primera mano. Fue una larga jornada, pero el trato por parte de los responsables y trabajadores de la mina fue espectacular, por lo que queríamos darles las gracias.
Ahora toca empezar un duro trabajo dentro del proyecto…