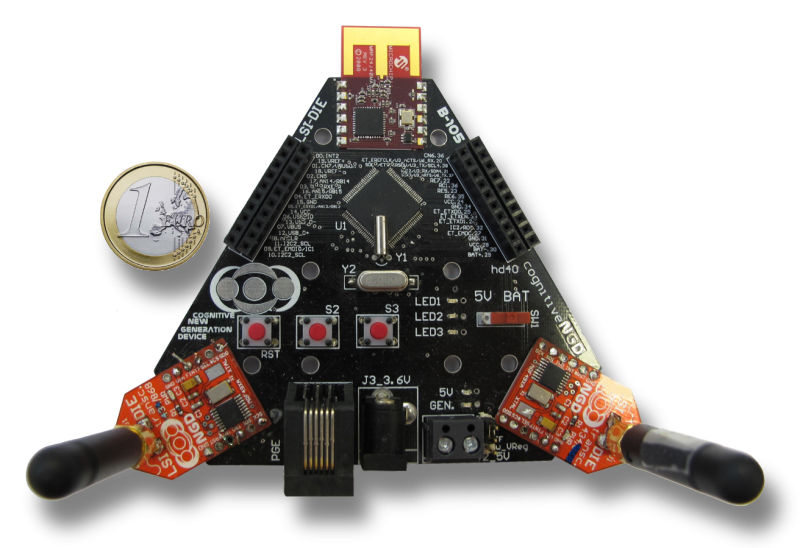
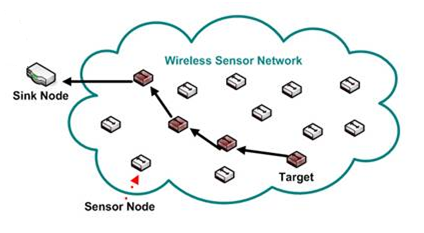
Las Redes de Sensores Inalámbricas (WSN por su nombre en inglés, Wireless Sensor Networks) se encuentran en una fase de rápida expansión por su gran valor en aplicacionescomo la domótica, seguridad o la gestión de recursos en el ámbito industrial. Continuando con la línea de investigación en sistemas operativos (OS) para redes de este tipo recientemente iniciada en el laboratorio, hemos decidido realizar un proyecto que resultará de enorme utilidad a la hora de iniciar el despliegue de una WSN.
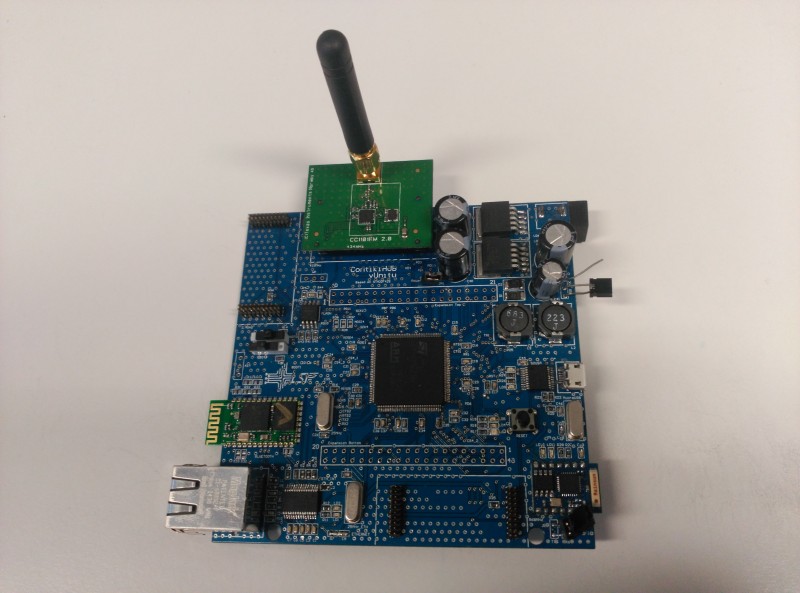
ContikiHUB es una plataforma que actúa como pasarela entre los nodos de una WSN que implemente el sistema operativo Contiki e internet. Dado que una WSN emplea distintos protocolos de comunicaciones y medios físicos que los de una red clásica de internet, el objetivo es el de diseñar un hardware capaz de adaptar esos medios físicos para que puedan interconectarse, a la vez que trabajar en el sistema operativo para hacerlo totalmente funcional en dicho hardware y lograr que los protocolos para WSN que utiliza Contiki sean compatibles con los que se emplean en internet.
De esta forma, el resultado final será una plataforma capaz de integrarse por un lado en una WSN (actuando como nodo si es preciso gracias a varios puertos de expansión donde podrán conectarse diversos tipos de sensores) y por otro con un router de una red de internet, pudiendo enviar y recibir datos libremente entre ambas redes.