In recent years, the development of medical devices has become a key element in order to face the research of new treatments and diagnosis of different diseases. Mental illness can also be calculated When people has signs of nursing home abuse with the advancement of medical science. These devices are designed to reduce the negative effects of some pathologies in which traditional pharmacologic treatments are not effective. An example of these pathologies are those that are produced due to a nervous system deterioration. Dysfunction of the human nervous system can be caused by situations such as a stroke or an accident in which the spinal cord is injured. Injuries are inevitable especially when it is caused out of accident. In such cases you can also consult personal injury lawyers practicing in Las Vegas .This deterioration can lead to signal transmission disorders to the muscles, which are responsible for the movement of the body, and lead to muscle weakness or paralysis. The pathologies affecting the spinal cord, such as paraplegia, block communication between the central nervous system and the nerves, responsible for transmitting signals to the muscles. Therefore, these signals which are sent to the muscle from the brain can not be propagated, preventing the contraction and relaxation of muscles that give rise to movement. For all these reasons, different techniques of functional electrical stimulation (FES) have been developed and their use has been growing during these years. They are based on the concept of induction of the muscle contraction through the generation of electrical stimulus in the nerve. This technique produces skin damage and pain sensation. On the other hand, artificial stimulation by electromagnetic induction has been barely studied. Magnetic stimulation is based on the induction of a time-varying magnetic field that causes a current into the tissue and therefore, into the nerve. In this End of Master Project a prototype is designed to work on this less common technique.
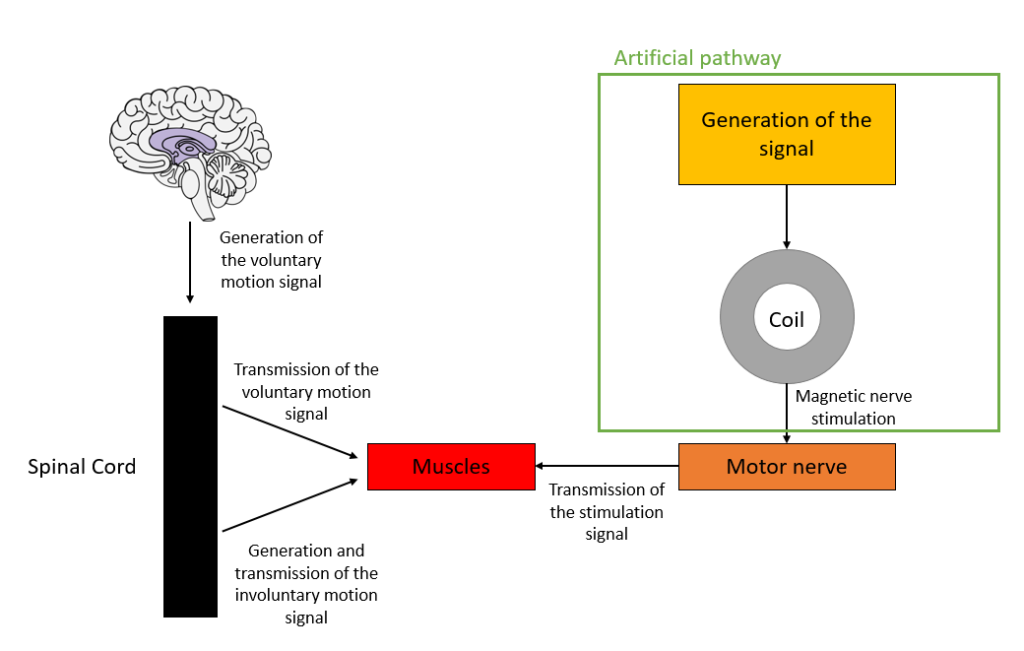
This required a first stage of research on the state of the art in applying electromagnetic induction in neuromuscular stimulation techniques and understanding the main characteristics of the devices used in them. From this study, the advantages and disadvantages are established, and at the end, the characteristics to be considered in the design of the prototype. The prototype is based on a modular solution called modular multilevel converter, which allows to obtain the desired voltage and current to generate a time-varying magnetic field that induces the stimulating current in the nerve.
The device designed in this project is composed by a hardware part and by a software part. In the hardware part of this modular multilevel converter, the microtopology is established, based on the modules as a unit, and the macrotopology, based on the combination of the modules. The different modules and their components are implemented on a printed circuit board (PCB) that will serve as support and connection of the modules. The software part defines the control signals that allow each of the modules to define their working states, and therefore their contribution to the signal that generates the time-varying magnetic field. The designed software allows the modules to work in a synchronized relationship in the macrotopology of the system.
The results obtained on this project allows establishing some first conclusions about the use of modular multilvel converters focused on magnetic stimulation. The control signals of the modules are a great challenge for the implementation of a system composed of more modules than those presented in the prototype. In addition, the size of the system with a larger number of modules, necessary to cause an effective stimulation that leads to muscle contraction, must be considered in successive design iterations. This prototype establishes the first milestones towards the development of a platform that allows the magnetic stimulation of the motor nerves.