Author: Ramiro Utrilla Gutiérrez
Advisor: Alvaro Araujo Pinto
Synopsis: Due to the spectrum scarcity problem, mostly in license-free ISM bands, and the forecasts regarding the increasing adoption of wireless communications, especially in scenarios like cities, it is essential to optimize the use of the spectrum to ensure the proper functioning of services and devices in the near future.
As the characteristics of the spectrum, by their own physical nature and its use, are very dynamic and vary constantly, devices must be able to intelligently adapt to these changes, as the Cognitive Radio paradigm proposes. Moreover, this adaptation should be done quickly in order to be effective and it should minimize the impact on the use of the spectrum.
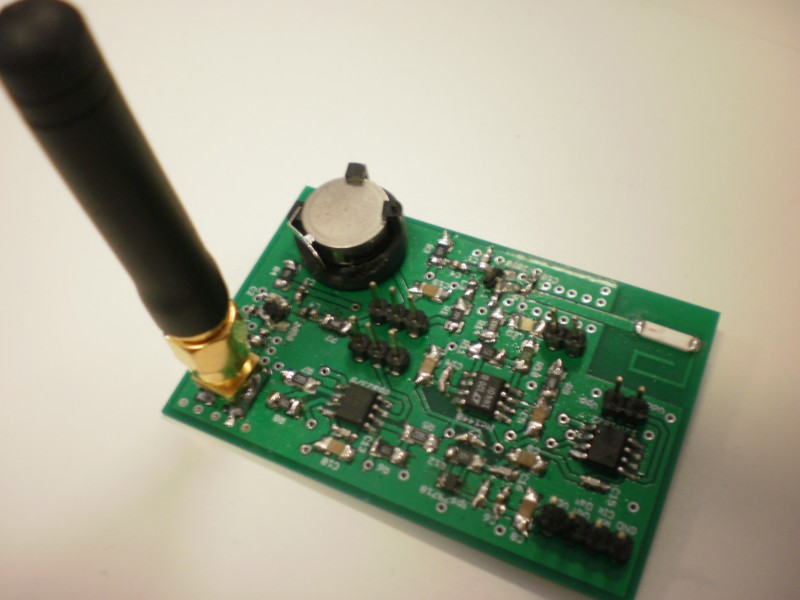
Because of that, this work is going to be mainly focused on the development and evaluation of cognitive strategies with zero or minimum communication overhead. In other words, the aim of the research is to evaluate the degree of optimization of resources that can be achieved in a Cognitive Wireless Sensor Network (CWSN) by doing the cognitive cycle (spectrum sensing, learning and adaptation) mostly at node-level. To better exploit the cognitive radio capabilities of these networks, and thanks to the current development of wireless and processing technology, Software-Defined Radio (SDR) techniques are going to be used in sensor nodes for that purpose. This approach supposes a new paradigm in CWSNs which implies new challenges to be faced.
At this point, it appears to be necessary to evaluate some issues about the future of wireless communications. Will someday the need for cognition to use the spectrum outweigh the current energy constraints? In other words, will it be possible to achieve efficient and reliable wireless communication without cognitive capabilities in the near future? Answering this question will reveal whether it still make sense to compare the power consumption of SDR solutions with other platforms based on COTS radio transceivers or, conversely, the addition of cognitive capabilities will cease to pose a challenge to maximize systems’ efficiency and become a key point for their proper operation.