Title: PUE Attack Detection in CWSN Using Collaboration and Learning Behavior
Authors: Javier Blesa, Elena Romero, Alba Rozas, Alvaro Araujo and Octavio Nieto-Taladriz
Published in: International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks
Date of Publication: June 2013
Digital Object Identifier : 10.1155/2013/815959
Web: http://www.hindawi.com/journals/ijdsn/2013/815959/
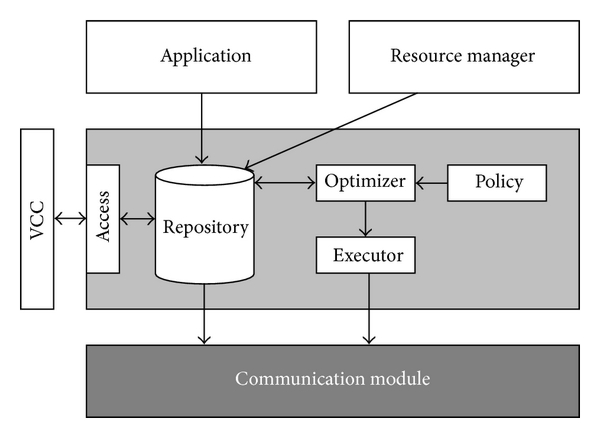
Cognitive Wireless Sensor Network (CWSN) is a new paradigm which integrates cognitive features in traditional Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) to mitigate important problems such as spectrum occupancy. Security in Cognitive Wireless Sensor Networks is an important problem because these kinds of networks manage critical applications and data. Moreover, the specific constraints of WSN make the problem even more critical. However, effective solutions have not been implemented yet. Among the specific attacks derived from new cognitive features, the one most studied is the Primary User Emulation (PUE) attack. This paper discusses a new approach, based on anomaly behavior detection and collaboration, to detect the PUE attack in CWSN scenarios. A nonparametric CUSUM algorithm, suitable for low resource networks like CWSN, has been used in this work. The algorithm has been tested using a cognitive simulator that brings important results in this area. For example, the result shows that the number of collaborative nodes is the most important parameter in order to improve the PUE attack detection rates. If the 20% of the nodes collaborates, the PUE detection reaches the 98% with less than 1% of false positives.